Knee pain - causes prevention and treatment. Which diseases cause joint pain?
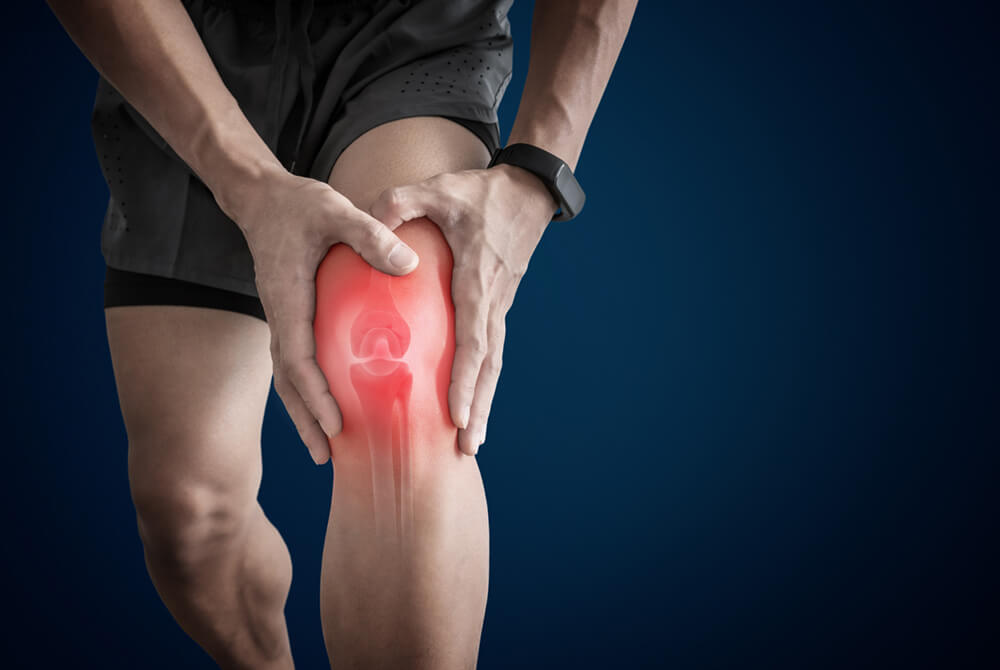
Knee pains are among the most common joint pains. Their causes can have various origins - resulting from injury, overload, arthritis and disease. Knee pain is usually suffered by the elderly, physically active people and up to two-thirds of overweight and obese people. What do the different types of knee pain suggest? How can it be prevented?
Knee pain - the most common causes
Knee joints are extremely vulnerable to strain and injury, which means that almost everyone can suffer from knee pain, although the causes will vary. Painful knees are a common problem. Unfortunately, they are also often ignored until they become more severe, making everyday life more difficult.
Knee pain can be either severe, caused by trauma, or chronic, caused by strain, degeneration or ligament damage. If knee pain does not go away on its own, it should be looked at more closely, try to determine the cause and take steps to eliminate or treat it. Where do knee pains come from?
Knee pain and obesity
Knee joints often bother people who are overweight and obese. As many as two thirds of them report problems with a painful knee. Excess body weight causes tremendous overload on the knees and leads to joint degeneration as a result of too much pressure, but also inflammation, which is encouraged by obesity.
Causes of knee pain in old age
It is natural that as we age, there is an increasing degeneration of cartilage and bone tissue as well as muscle weakness. The knee joint, like others, becomes worn out with age.
Knee pain vs. inflammatory and rheumatoid diseases
Numerous diseases can lead to knee injuries. The best known is rheumatoid arthritis, but only among inflammatory diseases are more than 200 entities in which knee pain is a symptom. Knee pain can also occur as a result of a bacterial infection of the joint.
Injuries that cause knee pain
A common cause of knee joint injuries is the practice of sports, especially team sports and skiing. With the high dynamics of movement and physical contact between athletes, it is easy to twist the knee excessively, which leads to stretching, tearing or rupturing of the anterior cruciate ligament - the main knee stabiliser. An injury to the ligament, in addition to knee pain, is accompanied by swelling of the knee. Other injuries responsible for suffering knee pain are damage to the meniscus and articular cartilage..
Recommended products
Overload knee pain in sport
Overload knee pains are chronic aches that result from multiple micro-injuries. Among physically active people, the most common type of knee pain are so-called:
- Runner's knee - knee pain is located at the front, near the kneecap. It occurs in people who start a physical activity or increase the intensity of their workout. Knee pain occurs after running, when climbing stairs, performing squats and sitting for long periods of time.
- Jumper's knee - knee pain is located at the lower part of the kneecap, at the point where it joins the ligament. The pain occurs at the beginning of activity and afterwards, or, when the injury is more advanced, also during everyday activities such as squatting, kneeling and climbing stairs.
Types of knee pain
Knee pain can be very varied. Its location, type and duration can signal a variety of health problems. The following types are distinguished:
- knee pain when bending, which can be the result of injury, degenerative changes or synovial deficiency. The latter is accompanied by a characteristic crackling sound, e.g. when squatting.
- knee pain after prolonged immobilisation, after sleeping or sitting, accompanied by stiffness usually occurs in elderly people and is a result of joint degeneration.
- pain under the knee at the front can occur in physically active people, but also obese people.
- pain under the knee at the back is usually associated with degeneration of the knee joint.
- knee pain on the inside signals degenerative changes.
- pain in the knee on the outside is often due to rheumatoid arthritis.
As you can see, it is impossible to attribute a specific condition to a particular type of knee pain. A doctor's visit and diagnostic - X-ray, ultrasound or more advanced methods - are required to determine the exact cause of the problem.
How to treat a sore knee?
The treatment of a painful knee should be determined by a doctor. Do not delay visiting a specialist if the knee pain does not go away on its own, gets worse, or is accompanied by swelling, pain, redness or problems with movement.
A popular statement "Prevention is better than cure" also applies to knees. Not all knee joint changes can be prevented, but many of them may be influenced through our lifestyle.
Prevention of knee pain
The basis of prevention should be to maintain a healthy body weight so as not to lead to joint degeneration due to too much pressure. The second point is moderate physical activity to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee joints. Strong muscles relieve pressure on the ligaments and help prevent the occurrence of knee pain. Supplementation with high-quality products can also help to prevent knee pain of various origins. These should contain substances with effects demonstrated by scientific studies and in concentrations that can show a beneficial effect in relieving knee pain. These supplements include chondroitin, glucosamine, collagen, hyaluronic acid, boswellic acid and MSM sulphur.

Knee pain treatment
Treatment of painful knees usually starts with externally applied cooling agents and painkillers - ointments and patches, as well as taking common anti-inflammatory drugs. Saving painful joints and rehabilitation are of great importance.. One treatment method is to inject hyaluronic acid directly into the knee joint. In advanced lesions and many injuries, surgery is necessary.
Joint pain - what can cause it?
We have looked a little more closely at the subject of knee pain, but these are not the only joints that can hurt. In addition to knees, shoulders, hips, wrists and fingers are among the joints most commonly affected by pain. Joint pain after injury (e.g. severe contusions, dislocations) can occur repeatedly over many years and sometimes throughout life. In some diseases, pain in all joints occurs, indicating an inflammatory basis for the pain rather than a mechanical injury.
What diseases do joint pain occur with?
Viral infections are accompanied by the well-known feeling of 'breaking in the bones.
Lyme disease - one of the symptoms of the disease caused by a tick bite is joint pain.
Joint degeneration. Degeneration affects not only the knees but often also the shoulders and hips, joints that bear a lot of strain.
Rheumatoid arthritis, in which the small joints - fingers and wrists - usually hurt.
Gout. Joint pain in gout starts by affecting the joint of the big toe.
Psoriatic arthritis is an autoimmune disease that affects many joints. The pain may appear asymmetrically, for example in only one wrist.
Lupus erythematosus is another autoimmune disease in which joint pain occurs.
