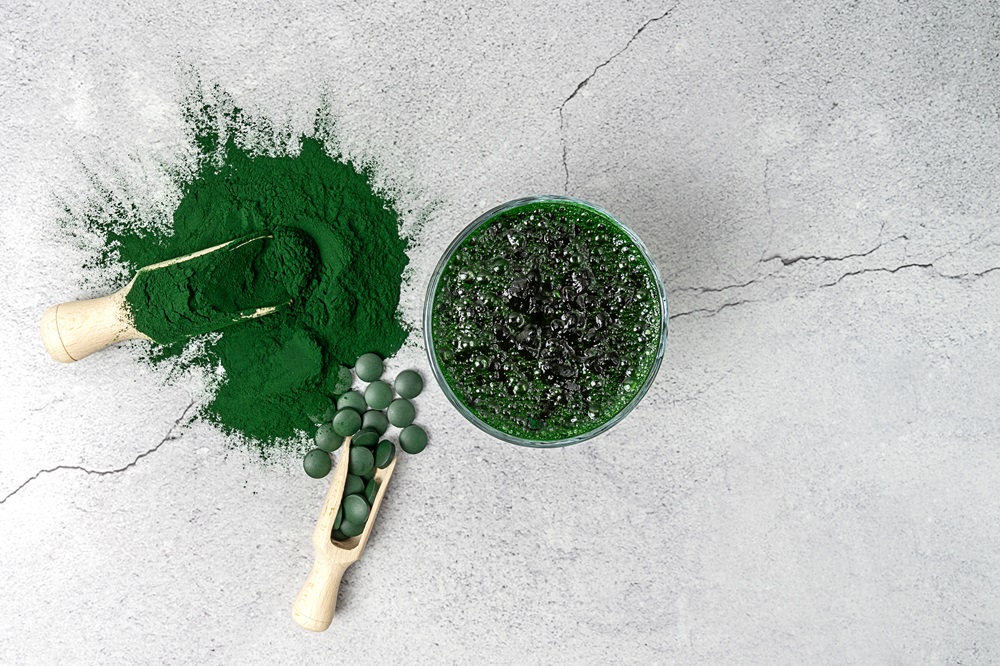
Spirulina is a microscopic algae that is becoming more and more popular all over the world. It is a cyanobacteria whose potential, health-promoting properties arouse considerable interest among scientists, making spirulina the object of numerous scientific studies. The analysis carried out so far suggests that green-blue algae may have a positive effect on the work of the cardiovascular system, and may also have a positive effect on carbohydrate metabolism and the process of weight reduction. What other properties does spirulina have? What nutrients does spiral algae provide? What is the use of cyanobacteria? Is spirulina supplementation safe?
Summary
Spirulina - what is it?
Spirulina is a multicellular, filamentous and prokaryotic algae with a green-blue colour, which is characterized by a spiral shape, to which it owes its name. It is an algae growing on clean and warm water reservoirs - the main habitats of the spirulina include the Pacific Ocean near Japan and Hawaii, as well as large freshwater lakes, such as Lake Chad in Africa, lake Klamath in North America or Lake Titicaca in South America. According to the current state of knowledge, the spirulina is characterized as a cyanobacteria of the genus Arthrospira, and spirulina is referred to as two species of cyanobacteria, such as Arthrospira platensis and Arthrospira maxim.
The history of the alga dates back to the Aztec era, and the collected data suggest that in the XVI century the spirulina was harvested from Lake Texcoco and consumed in present-day Mexico. However, on an industrial scale, the cyanobacteria began to be used in the 70s, and in 1967 the algae was recognized by the International Association of Applied Microbiology as a future source of food. In turn, the first dietary supplement containing the compound was introduced to the market in 1979.
The spirulina is increasingly used as an additive to various types of products. The microscopic algae is found in food, as well as in cosmetics or in the form of dietary supplements. The spirulina production takes place on special algae farms in countries such as the United States, Thailand, India, Japan and China.
Spirulina - nutritional values and composition
The spirulina, classified as a functional food, is more and more often referred to as super foods, which is due to the fact that the algae is distinguished not only by its interesting and intense taste, but also a wealth of valuable nutrients that are easily absorbed by the human body. It is an environmentally friendly algae that does not need fertile land and, moreover, is characterized by rapid growth and low energy needs. Growing the spirulina also requires much less water than soy or corn protein.
The presence of individual nutrients in the spirulina can vary depending on the area of its production, as well as the climate and salinity of the water. Harvesting procedures may affect the content of vitamins, minerals and phytochemicals in algae.
In the spirulina, can be found primarily a protein that accounts for about 70% of the dry weight of the product and is distinguished by a valuable amino acid composition, being a complete source of protein.
In addition, the cyanobacteria contain essential unsaturated fatty acids, such as gamma-linolenic acid.
It is a rich source of vitamins and minerals - among others:
- vitamin A,
- vitamin C,
- vitamins of group B,
- potassium,
- zinc,
- iron,
- magnesium,
- iodine.
Moreover, the spirulina contains significant amounts of chlorophyll, which is responsible for the intense colour of algae, as well as other phytonutrients, such as zeaxanthin, lutein or c-phycocyanin.
Read also: Superfoods - what is it? Is it worth using them?
Recommended products with spirulina
Spirulina - for what? Properties and effects of spirulina
The interesting composition of spirulina makes the algae more and more popular, not only among consumers, but also among scientists and researchers. Data so far suggest that the spirulina may have hypotensive properties, affecting blood pressure and contributing to a significant reduction in systolic and diastolic pressure, which may be due to the fact that the microalgae has the ability to release substances that can contribute to the expansion of blood vessels, and at the same time is distinguished by the potential to inhibit the secretion of compounds that are responsible for their narrowing.
The spirulina may also exhibit hypolipidemic properties, lowering total cholesterol and reducing LDL levels in the body, as well as contributing to the reduction of triglycerides and increasing HDL cholesterol levels in the blood serum. In addition, the ingredient may also have a hypoglycemic effect, helping to normalize blood glucose levels among people struggling with type II diabetes, which is probably due to the fact that, the spirulina can stimulate the secretion of insulin from pancreatic beta cells. Thus, it seems that the microscopic algae can be helpful in the prevention of metabolic syndrome.
What is more, the cyanobacteria of the Arthrospira genus may have antioxidant potential, neutralizing free radicals and reactive oxygen species and reducing oxidative stress, as well as delaying the aging process of the body. In addition, the spirulina may have anti-inflammatory effects, and may also have antimicrobial and antiviral effects, including by improving markers of inflammation, or inhibiting the expression and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, what may result from the presence in the spirulina of phenolic compounds, as well as phycocyanins. The microscopic algae can also have immunostimulating effects, and can increase the activity of macrophages and have a positive effect on the immune system, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria.
The cyanobacteria can also affect the brain, showing neuroprotective properties. Preliminary clinical studies suggest that the spirulina may reduce mental fatigue and have a beneficial effect on cognitive function. Some data also report that the green-blue algae may contribute to increased exercise endurance and improved performance among physically active people, even within a few hours after the first supplementation.
As if that were not enough, the substance can positively affect the composition of the intestinal microflora. In addition, according to the results of scientific research, it is considered that the spirulina supplementation may be helpful in the control and prevention of excessive body weight. The data obtained so far suggests that the spirulina may reduce appetite, as well as contribute to the reduction of waist circumference and body weight, as well as to the reduction of BMI.

Spirulina - use. Spirulina - for who?
The spirulina can be of biological and economic importance, as the algae has a wide range of use - the cyanobacteria are used in the food industry as well as in the pharmaceutical, biofuel, cosmetic and agricultural industries. The substance is used, among others, in the production of snacks and cookies, as well as in the production of functional drinks, dairy products, pasta, oils or dietary supplements. The spirulina is also used as a dye, as well as an ingredient in animal feed.
The spirulina comes in the form of powder, liquid, oil, tablets and capsules, helping to meet the demand for diversity while being a highly nutritious food and a source of valuable nutrients. The microscopic algae is recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) as one of the most important superfoods that is used by NASA during space expeditions, it can also help fight malnutrition in the world.
Spirulina - dosage and apply
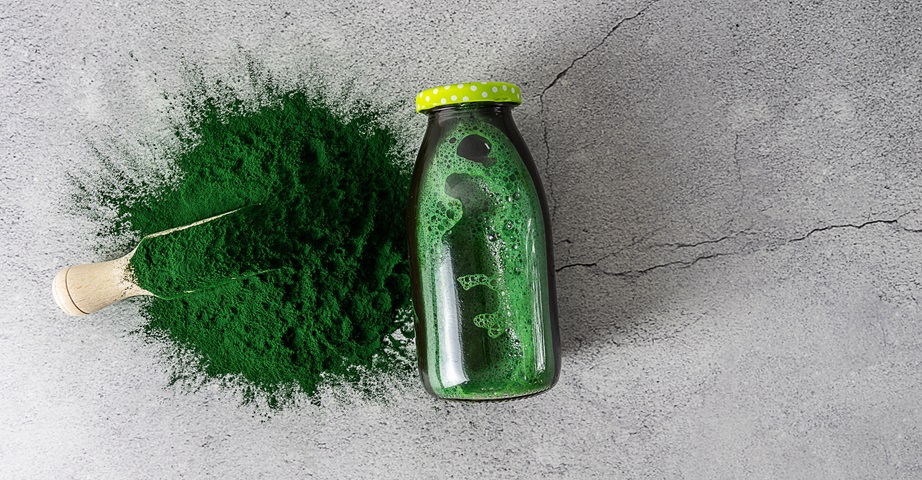
Dietary supplements containing the spirulina are most often available in the form of spirulina powder or in the form of tablets, which allows trouble-free use of the ingredient in the daily menu. The powdered spirulina can be used as an addition to cocktails, shakes, as well as sauces or sandwich pastes. It is worth paying attention to the fact that the green-blue cyanobacteria is distinguished by an intense aroma with a fishy aftertaste - for people who may be disturbed by the characteristic taste, a good solution may be to use the spirulina in the form of easy-to-swallow tablets.
Various doses of the spirulina are used in scientific studies, and some data suggest that a small portion of the ingredient may have a positive effect on the functioning of the human body.
Spirulina - how long to use?
The time of supplementation may depend on the purpose of using the spirulina - in scientific analyses, focusing on supporting the slimming process, the algae was taken for about 12 weeks, in turn in studies checking the effect of the compound on exercise endurance, the effects were observed just a few hours after taking the first dose of the preparation.
When deciding to use dietary supplements containing cyanobacteria of the Arthrospira genus, it is worth reaching for proven preparations and following the manufacturer's guidelines, paying attention not to take the spirulina in excessive amounts.

Spirulina - contraindications and side effects
The spirulina is an ingredient that occurs naturally in nature, which is why supplementation with the cyanobacteria is considered safe for human health and should not contribute to the occurrence of adverse effects. Some data suggest that at the beginning of supplementation, mild digestive ailments such as flatulence or gases can be observed, but the symptoms disappear after a short time of using preparations with the spirulina.
Because the microscopic algae is a source of iodine, people struggling with hyperthyroidism should be especially careful. Dietary supplements containing the spirulina should be abandoned by people allergic to seaweed or seafood, as well as people who suffer from blood clotting disorders, from autoimmune diseases or phenylketonuria.
It is worth remembering that preparations rich in the spirulina, although they can provide the human body with significant amounts of valuable ingredients, will not replace a healthy and balanced menu, but only can be a valuable supplement to the diet. In addition, if you have any diseases or ailments, before using the spirulina preparations, it is worth consulting your doctor to discuss possible interactions of the cyanobacteria with the drugs, which you are taking.
Bibliography: