Collagen for joints - what to choose and how to use?

Collagen is a structural extracellular protein, which is the basic building block of the connective tissue of the human body. Lowering its content in the body causes an increase in mechanical load, which contributes to the degeneration of joints and the development of inflammation. If you train professionally or amateur sports, collagen plays a particularly important role in maintaining the health of joints, muscles and tendons. Can regular collagen supplementation have a positive effect on the musculoskeletal system? How to choose the best absorbable collagen for joints for athletes?
Summary
- How does collagen work on joints?
- Collagen or glucosamine – which is better for joints?
- What type of collagen is best for joints?
- How long to apply collagen on the joints to see the effects?
- Recommended daily intake of collagen for joints
- Collagen for joints for athletes - support during intensive training
- Good collagen for joints - what preparation to choose?
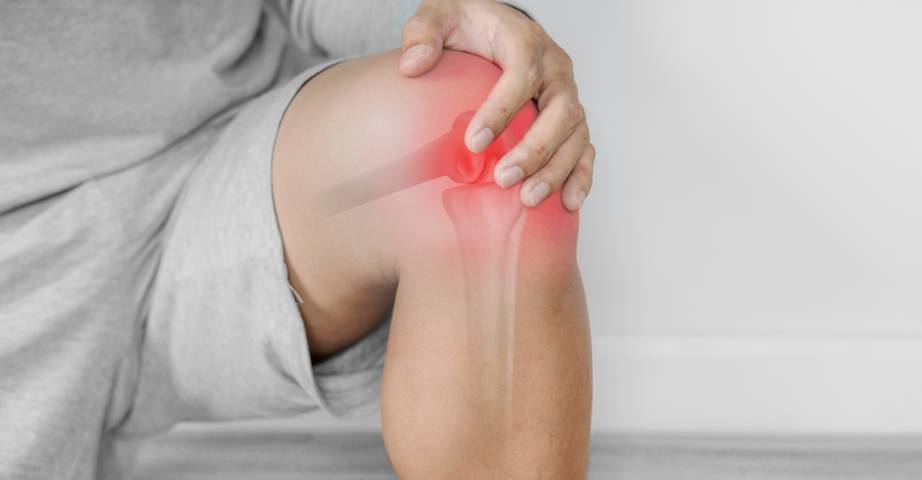
How does collagen work on joints?
Collagen is a fibrillar protein that makes up about 30% of all proteins that create the human body. It is found in the skin, bones, tendons, muscles, teeth and walls of blood vessels. With age and with intense physical exertion, the ability to synthesize collagen decreases, and its lack can cause the appearance of joint pain and deterioration of mobility. That is why dietary supplements with collagen are very popular among athletes and physically active people.
Does collagen help the joints? Such a question very often arises in the context of caring for the musculoskeletal system. The effect of collagen protein on the joints has been thoroughly studied. The collagen may increase the integrity of cartilage, because the decreasing with age concentration of this compound in the body is often associated with degenerative changes in the joints. The use of collagen preparations may also be helpful in maintaining the optimal amount of synovial fluid, which prevents abrasion of joint structures against bones.
Collagen or glucosamine – which is better for joints?
People who want to support the proper functioning of the joints can reach not only for dietary supplements with collagen. On the market, there are also preparations containing glucosamine, which is usually found in them in the form of glucosamine hydrochloride or sulfate. This compound is often used in combination with hyaluronic acid, the largest amounts of which are found in the skin, synovial fluid and the vitreous body of the eye.
What to choose for joint support and protection of joint cartilage: glucosamine or collagen? The answer to this question is not clear. In a situation where the problem is the lack of elasticity of the ligaments, it is better to decide to take collagen. On the other hand, if joint pain symptoms and difficulty moving the knees are caused by a deficiency of synovial fluid, then glucosamine can help.
Recommended products with collagen
What type of collagen is best for joints?
Due to the structure and functions performed in the body, are distinguished more than 20 types of collagen protein. The most popular of them is type I collagen, which accounts for nearly 90% of all collagen fibres. It is responsible for maintaining healthy skin, hair and nails. Type II collagen is also very common, which determines the health of the entire locomotor system. It is part of the cartilage in the joints, and its deficiency can cause joint pain and joint stiffness. Therefore, good collagen for joints should contain collagen protein type II.
How long to apply collagen on the joints to see the effects?
The first step you should take to supplement the level of collagen in the body is a balanced diet containing products rich in natural collagen. These include, among others, decoctions of chicken feet, jelly from legs, pork shanks, offal. The amount of collagen in food is often insufficient to meet the needs of the body. In such cases, collagen supplementation may be a good solution. It is often recommended for athletes and physically active people, as it can be of great importance in preventing the formation of injuries and degeneration.
In order to feel the results of collagen supplementation, special attention should be paid to the type of collagen present in the preparation. Not without significance is also the presence of additional substances that can increase collagen production. These include, among others, such compounds as hyaluronic acid, chondroitin and glucosamine. The absorption of collagen is also dependent on vitamin C. For natural structural protein to have time to rebuild in the body, collagen supplementation should last a minimum of 2-3 months.
Recommended daily intake of collagen for joints
To see the effects of collagen supplementation, you should properly choose its portion to the needs of the body. Scientific studies suggest that the optimal amount of this protein is from 8 to 12 g per day. Such an amount is easiest to deliver by reaching for natural collagen on the joints in the form of powder or tablets.
Physically active people who often train and athletes practicing disciplines that require high joint strength have an increased demand for collagen. In this situation, the amount of collagen in the diet can be increased to 15 g per day.
Collagen for joints for athletes - support during intensive training
Athletes are a group of people who are more exposed to excessive use of cartilage, ligaments and tendons. This is mainly due to considerable biomechanical loads of connective tissue and non-physiological movements. For this reason, the collagen is recommended among all players exposed to overload. It can be used by both people overtraining, and athletes who spend too little time on regeneration or using incorrect techniques during training.
Collagen can be a valuable support in the diet of runners, cyclists, triathletes. The optimal amount of this compound in the menu can protect the musculoskeletal system from overloads, support the regeneration of articular cartilage and promote the improvement of joint mobility. Supplementation allows to supplement possible deficiencies of collagen protein, which results in a well-functioning musculoskeletal system better prepared to undertake intense physical activity.
Good collagen for joints - what preparation to choose?
Choosing the right dietary supplement with collagen depends primarily on the taste preferences and individual needs of the body. The most recommended collagen for joints is hydrolysed collagen, which is distinguished by high bioavailability. It contains a protein that has been hydrolysed, which is broken down into smaller molecules using water and appropriate enzymes. Supplementation with preparations containing hydrolysed collagen is the best way to provide the body with a well-absorbed source of collagen protein.
The strongest collagen on the joints is type II collagen, which occurs, among others, in joint cartilage. This type of protein is essential to ensure the elasticity and durability of tissues covering the articular surfaces and to maintain healthy bones.
Fish collagen for joints – is it worth it?
Fish collagen is considered the best absorbable collagen for joints. It is obtained from scales and skins of fish such as cod, tuna, salmon, pollock. It is distinguished by a high content of collagen peptides and amino acids such as glycine, proline and hydroxyproline, which are the basic building blocks of protein. Fish collagen for joints is odorless and devoid of expressive taste, which makes it easier to add to drinks and meals.
Beef collagen for joints – what are the advantages?
Dietary supplements containing beef collagen are also very popular among athletes and physically active people. It is obtained from bovine connective tissue such as skin, bones and tendons. Bovine collagen contains collagen types I, II, III, V and X, so it can be a good choice for people who, apart from the cosmetic effect, would like to support the condition of connective tissue throughout the body. It will also be a good solution in case of hypersensitivity to protein derived from fish and seafood.
Collagen for joints to drink - is it more effective?
A common form of collagen that can be added to drinks, smoothies, and meals is collagen in powder. It gives you the opportunity to choose the taste and additional substances such as hyaluronic acid, vitamin C or organic sulphur. When choosing a preparation, be careful about additives in the form of sugar and sweeteners. Although its preparation for consumption requires a bit more time, it can be distinguished by a higher content of active substances.
Collagen for joints in tablets – convenient solution?
People who lead an intense lifestyle and often forget about daily collagen intake can reach for the supplement in the form of easy-to-swallow tablets. This type of preparation is easy to take and store. Collagen in tablets contains a precisely measured portion of collagen protein and allows you to provide the body with the desired amount of valuable ingredient.

Pure collagen for joints – what stands out?
Wondering what is the best collagen for joints, you need to know that this compound can occur in various forms and types. The most natural collagen for joints is hydrolysed collagen, which is distinguished by the highest bioavailability. Decomposition of long chains into collagen peptides and free amino acids may favourably affect its absorption and assimilability.
When choosing collagen for runners or endurance athletes, it is also worth paying attention to the type of collagen protein. People who want to improve the condition of joints, tendons and muscles, as well as reduce the risk of inflammation, should choose preparations with collagen type II, which is a key component of articular cartilage.
When choosing a supplement, it is also worth making sure that it contains only high-quality collagen, without the addition of artificial substances, preservatives and fillers. It is also important that it is free of heavy metals and tested by an independent accredited laboratory. Pure collagen for joints is primarily a proven and safe product in supplementation.
Collagen for joints - summary
Literature reports indicate that collagen supplementation may have a beneficial effect on joint structure, bone mineral density, as well as muscle regeneration processes. In addition, taking dietary supplements with this natural protein can help reduce pain symptoms in the joints and improve their mobility. However, it should be remembered that both the origin of collagen and its molecular structure have a significant impact on obtaining the above-mentioned effects.

